Comprehensive Guide to Alopecia Causes, 7 Types, and Latest Hair Loss Treatments
Alopecia is the medical term for hair loss and a highly prevalent dermatological condition that extends far beyond a simple cosmetic concern. This condition is not monolithic. It encompasses a diverse range of disorders that can affect the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair.
This comprehensive guide will dissect the fundamental causes of hair loss, detail the seven major types of alopecia, and explore the most current and effective medical, surgical, and supportive treatment options available for men, women, and children today.
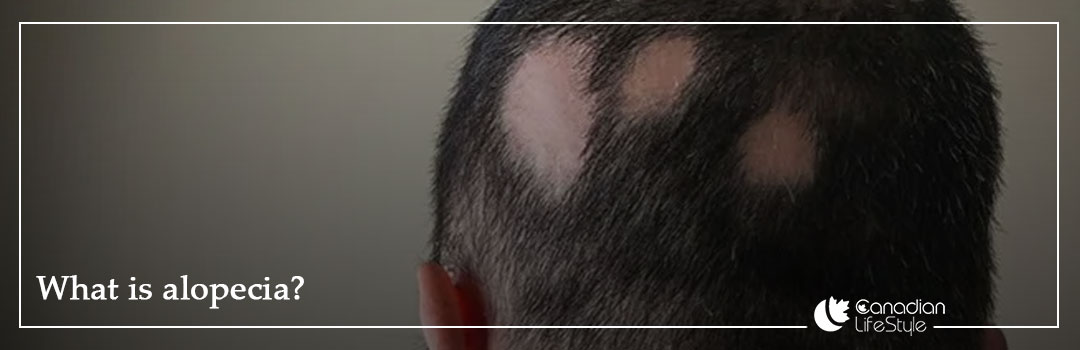
What is alopecia?
Alopecia is a kind of hair loss which can affect just the scalp including eyebrows, eyelashes and body hair. Alopecia can be temporary or permanent. In alopecia types, effluvium which is related to stress is temporary and scarring alopecia is known as a permanent model. This kind of hair problem can be a standalone condition or a symptom of an underlying medical issue. You should know that it’s pattern depends on the specific type.
Read more: Hair loss after 40
What causes alopecia?
To answer this question of what causes alopecia, we can say genetics and hormones. Another option is the immune system attacks hair follicles and causes alopecia. Actually alopecia can also be caused by nutritional deficiencies like iron deficiency. If alopecia is caused by the immune system, it means the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles. The most common cause of baldness is hereditary which is connected with genetics. As we said, nutritional deficiencies and medications like cancer treatments can cause hair loss too. Some kinds of lifestyle factors like smoking and having tight hair styles can cause this hair problem.
Read more: Beauty Pricing
Alopecia treatment
Alopecia treatment is not very easy and simple and the people who struggle with this problem should talk with a dermatologist to discuss the best treatment options because treatments are not always fully effective for everyone. We have topical medication, oral medication, surgical and emerging.
In topical medication, doctors advise to use minoxidil which is a vasodilator that increases blood flow to the scalp and extends the hair growth phase.
In oral medication, dermatologists prescribe finasteride which blocks the enzyme 5 alpha reductase, which converts testosterone to the follicle damaging hormone DHT. This prescription is only for men and highly effective at halting hair loss. Women who are or may be pregnant should not use it.
Surgical treatment includes hair transplantation and relocates permanent hair follicles from the back sides of the scalp to the thinning or bald areas.
Emerging treatment category done by low dose oral minoxidil and used off label in a low dose pill form and often used for patients who dislike topical application. Both men and women can deal with this problem by emerging treatment categories. Finding the right, gentle hair products is key; you can explore specialty retailers or an online beauty store with global shipping for wide access to treatments.
Read more: Oily Skin Routine Products
Alopecia treatment at home
Alopecia treatment at home is not normally recommended by dermatologists as a primary or standalone solution due to the complexity and varied causes of hair loss. We know it as supportive therapies too. Popular natural methods like using rosemary oil, pumpkin seed oil and aloe vera as home remedy for alopecia treatment at home. People who struggle with any kind of alopecia, should manage stress. Having a balanced diet and using supplements can be effective too. Using supplements like biotin, iron, zinc and omega-3 can be useful too. While focus is on the scalp, addressing general hair health concerns like Split Ends can improve the overall appearance of remaining hair.
Alopecia treatment for kids
Treating alopecia in children requires a highly careful approach. Actually the treatment plan largely depends on the child's age, the extent of hair loss and the type of alopecia which alopecia areata is the most common type in children.
For example, topical corticosteroids are often the first choice for young children. The mechanism is by using potent creams or solutions applied to the bald patches.
Dermatologists often use topical minoxidil as an adjunct. It will stimulate blood flow and prolong the hair growth phase.
Read more: How to Store Cosmetics
Alopecia treatment for men
Alopecia treatment for men is highly dependent on the hair loss caused by genetics or autoimmune. For example, androgenetic alopecia which is known as male pattern hair loss, is the most common form driven by genetics and the hormone dihydrotestosterone. Alopecia treatment for men includes oral medication, topical medication and combination therapy.
Reed more: Benefits of Iron Supplements for Skin, Hair, and Nails
7 types of alopecia
Now we want to talk about 7 types of alopecia called alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, traction alopecia, anagen effluvium, lichen planopilaris and frontal fibrosing alopecia.
| Alopecia type |
Introduction |
Cause by |
Appearance |
| androgenetic alopecia |
The most common type |
A combination of genetics and the hormone |
diffuse thinning over the top of the scalp |
| alopecia areata |
An autoimmune disorder |
Autoimmunity |
presents as smooth, round, patchy areas of hair loss on the scalp |
| telogen effluvium |
A temporary condition characterized by excessive shedding of hair |
A disruptive internal trigger |
Generalized thinning, not bald patches |
| traction alopecia |
Hair loss caused by prolonged tension |
Constant pulling from tight hairstyles |
Patchy hair loss often seen around the hairline and temples |
| anagen effluvium |
Rapid, extensive hair loss |
An agent that quickly and abruptly stops the mitotic |
Widespread shedding, often affecting the entire scalp and body |
| lichen planopilaris |
A rare inflammatory scarring alopecia |
Unknown, but believed to be an autoimmune attack |
Hair loss often presents as small, irregular patches |
| frontal fibrosing alopecia |
A type of scarring alopecia |
autoimmune and potentially hormonal factors. |
Characterized by a receding hairline |
Is alopecia permanent?
No, alopecia is not always permanent. You should know that the permanence of hair loss depends entirely on the specific type of alopecia you are dealing with and whether or not the hair follicle itself has been permanently damaged. Alopecia is divided into two major categories called non scarring and scarring. For example alopecia areata is often temporary, telogen effluvium is temporary, androgenetic alopecia is permanent without treatment and traction alopecia is potentially reversible. Careful product selection is vital, as scalp conditions like Dandruff or using harsh chemicals can exacerbate hair thinning.
Conclusion
Alopecia is more than just a cosmetic concern. It's a complex dermatological condition with profound psychological impact. From the temporary shedding of Telogen Effluvium to the permanent damage caused by Scarring Alopecia, the landscape of hair loss is diverse, driven by genetics, hormones (like DHT), and the immune system. Actually facing alopecia means embracing a path of proactive care. The most important step in alopecia treatment is seeking advice from a dermatologist. When seeking complementary products, look for quality and sustainability; consider options from an eco-friendly cosmetics store . Knowledge is the key to control and transform what feels like an uncontrollable condition into a manageable chapter. Exploring higher-end options, such as those found in Affordable Luxury Skincare , can also provide gentle and effective support.